Engagement
Engaging partners, agencies and community based organizations is critically important to ensure support and alignment for the RCIS and its implementation.

Effective engagement is key to a successful RCIS
The benefit to having a robust engagement process is having a better RCIS that builds relationships, identifies partners, contains better data/analytics and promotes equity and environmental justice. Key to designing a successful engagement process involves clearly articulating the purpose and goals for the RCIS; defining requirements for the RCIS and recommendations coming from the work; and using a structured engagement process and organization structure to best address audience/stakeholder needs and concerns.
-
Why is Engagement important?
- Understand needs of users/potential users - Increases the relevance and sensitivity of the strategy - Ensures that the process and products address equity and environmental justice
-

How does the Engagement process work?
- Helps identify and build relationships and partnerships - Incorporates the best data and analytical approaches - Encourages reflection and respect of community voices - Governance structure that defines roles and responsibilities of participants
-

Who is included in the Engagement process?
- Community voices - Partners - People and Organizations that will be impacted by the RCIS, such as farmers, infrastructure agencies, tribal groups
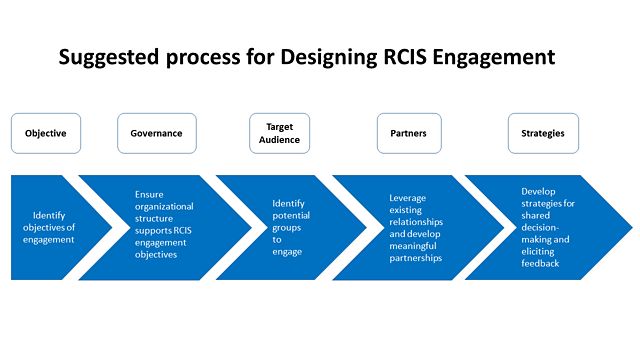
Graphic depicting suggested process for designing RCIS engagement. The process steps include objective (identify objectives of engagement); governance (ensure organizational structure supports RCIS engagement objectives); target audience (identify potential groups to engage); partners (leverage existing relationships and develop meaningful partnerships); and strategies (develop strategies for shared decision-making and eliciting feedback).

RCIS Management Model
Outlines an example of how to manage RCIS Strategy draft development and engagement work. Describes the roles and responsibilties for RCIS teams involved in the process.
- Core Team
- Technical and Science Advisors
- Steering Committee
- Interested parties
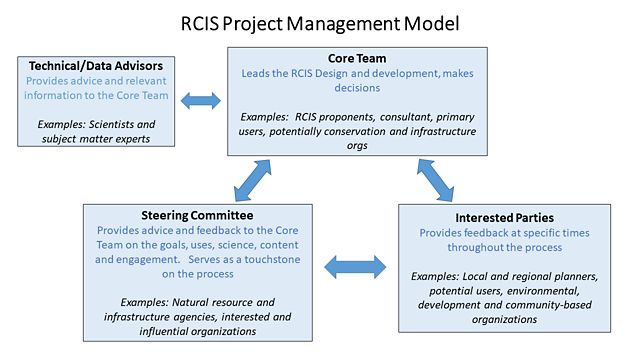
Graphic depicting RCIS project management model. Components include technical or data advisors, who provide advice or relevant information to the core team; the core team, who leads the RCIS design and development and makes decisions; the steering committee, who provides advice and feedback to the core team; and interested parties, who provide feedback at specific times throughout the process.
Partners for Engagement
Who do you need to reach and how to you engage them?
List of agencies and organizations that can play an important role as either a partner to enpower as a decision maker, engage or inform the RCIS Strategy
- Conservation organizations/practitioners
- Local governments and planners
- Natural resource agencies
- Public infrastructure agencies (transportation, water, flood control)
- Tribal groups and Indigenous communities
- Environmental justice groups and NGOs
- Local or regional habitat agencies (e.g. NCCP/HCPs)
- Infrastructure and environmental consultants
- Developers (renewable energy, housing)
- Funders
- Elected officials
Below is an outline of the types of questions for decision makers, users and other partners to consider in designing and executing an engagement plan.
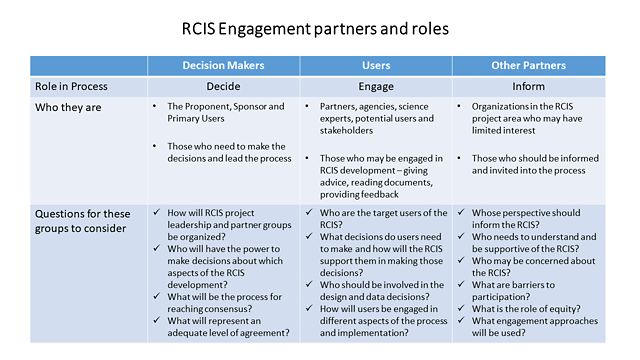
This table depicts the partners and roles in RCIS Engagement. The partners include decision makers, users, and other partners, whose roles in the process are to decide, engage, and inform, respectively.

Learn more about designing and implementing an RCIS Engagement strategy
The attached presentation provides details about why engagement is important, designing engagement, communication, implementation and centering equity.
